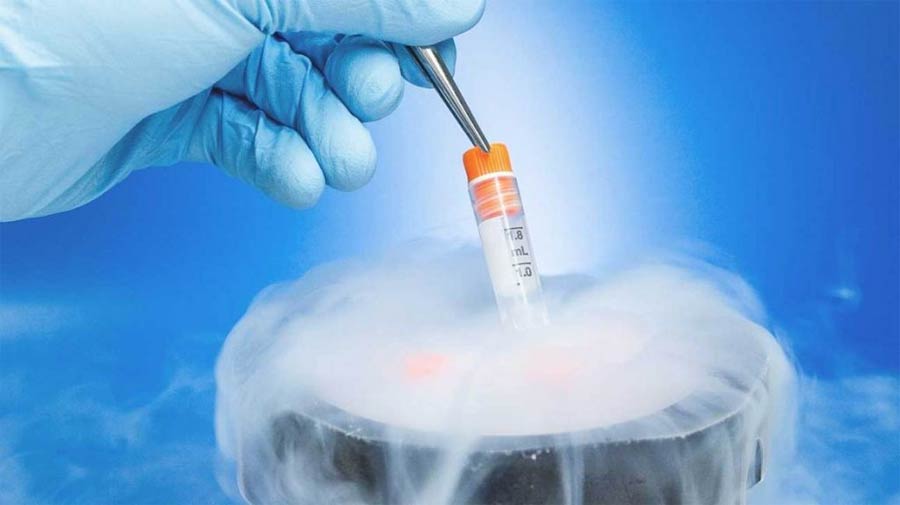
General principles of embryo freezing
The embryo freezing protocol offers a successful assisted reproductive laboratory infertile couple the possibility of multiple attempts close to the fresh cycle pregnancy rate. However, some reduction in implantation rate can be seen compared to the fresh cycle and some reduction should be considered normal. Studies claim that freezing and thawing of second-day embryos reduces the expected implantation rate of blastomeres lost by an average of 30%. Freezing and thawing processes have become one of the criteria that the couple considers when choosing between assisted reproduction centers.
Although the first baby born by thawing the frozen embryo was from a blastocyst in 1985, in which glycerol was used as a preservative, the success rates of zygote and early embryos in which propanediol and sucrose are used today are higher than the others in freezing and thawing.
Freezing of embryos from day one to three;
The early period embryos that have good quality are selected for freezing. It should be remembered that embryos with a single number of blastomeres may have entered the mitosis stage and therefore may be more easily exposed to strand damage by freezing, which may cause chromosomal organization disorders in the future.
Thawing of embryos from day one to three;
It is done under a laminar flow cabinet and at room temperature. The goal is to minimize possible damage by providing a slow and gradual transition of the embryos from the solid phase to the gel. The thawing process can be done on the same morning with a different method, or it can be done the day before the embryo transfer and the embryos with increased blastomere number can be transferred to the next day. After thawing, blastocyst transfer can also be performed with long-term embryo culture.
Blastocyst embryo freezing;
Blastocyst freezing pack is used in blastocyst freezing. All processes are done at room temperature and 5% CO2 environment. Embryos are rapidly placed in liquid nitrogen.
Blastocyst embryo thawing;
A blastocyst thawing pack is used. The tubes removed from the tank are quickly brought to room temperature. Meanwhile, the hands are used for heating. Once thawed, the contents are kept in the first and second solutions for 10 minutes each. They are incubated in blastocyst culture medium for 3-4 hours before the transfer.
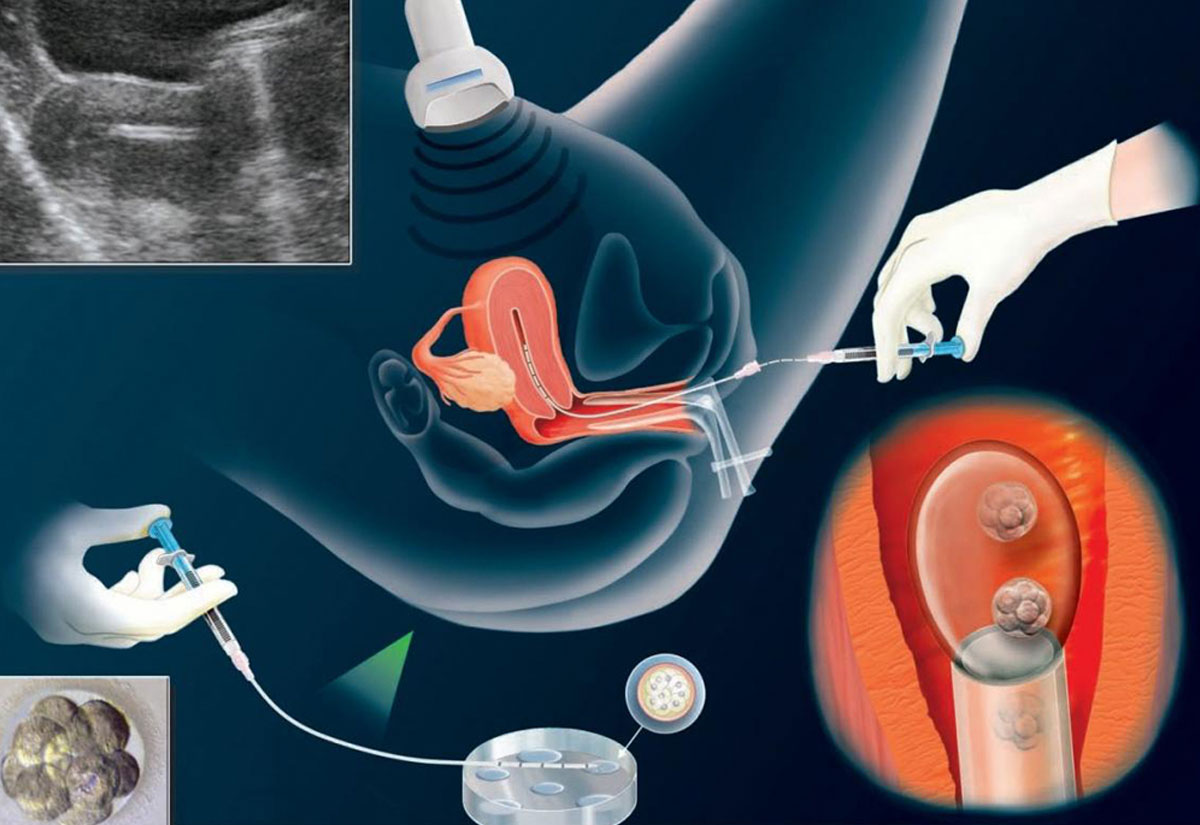
Frozen Embryo Transfer
For embryo transfer in frozen embryos, the uterine thickness of the mother is prepared after an average of three weeks of treatment, which starts with the second or third day of the IVF mother’s menstrual period. Embryos are made ready for transfer by the embryology laboratory for embryo transfer. After the expectant mother is taken to the table on the day of transfer, the embryos are taken into the catheter and injected into the uterus with the help of ultrasonography from the abdomen with a thin catheter. The drugs that the expectant mother will use are reminded again by the IVF nurse. By explaining to the expectant mother, she can be discharged from the clinic after her rest. She can give a pregnancy test 10-12 days after the transfer. You can consider frozen embryo transfers as normal embryo transfers.